Publicly expressing Black pain can render reactions of solidarity, healing, and empowerment, or exhaustion, guilt, and helplessness. However, Black voice can be a powerful instrument of change—used as a currency to be saved or spent or as a carrier of demand and solution. The past year has unearthed untold knowledge that gives additional context to the root of what drives this voice—its trauma, its demands, and its joy. Making this knowledge more public can help to inform how we understand and engage one another; how we reframe harmful Black narratives that shape the public perception; and how the power of Black creativity and resiliency as a political device can produce spaces of Black-centered freedom and liberation.
This essay and the corresponding collages aim to represent and make public the confrontation of pain and quest for joy found in the Black public realm of Chicago’s Mid-South Side. Each collage illustrates the relationship between publicness for Black Americans and the current urban landscape of vacancy including southern migration in response to public denial; the public scars left by urban renewal’s land mutilation; and the relentless pursuit of public freedoms in the public realm. The series offers a reflection on the contests that exist over land, space, and place alongside the aspiration of Black Americans to simply occupy and be carefree in public, unencumbered by fear and liberated from self-consciousness.
The collages include present-day mapping, photography, and historic images, in combination with clippings from, and references to, the imagery and symbols of Chicago’s Black life and prosperity used in the work of notable African American artists. My objective was to create new portrayals of the South Side and its people by making public some of the lesser-known narratives about these neighborhoods over the last century.
The narratives, rooted in the ownership and occupancy of land, reveal the practices of institutional racism, exclusion, and extraction, juxtaposed against images of the undiminished spirit, ambition, productivity, and creativity of Black Chicagoans. Richard Wright describes this as the “extremes of possibility” in his introduction to Black Metropolis: A Study of Negro Life in a Northern City, the seminal 1945 book by University of Chicago researchers St. Claire Drake and Horace A. Cayton on Negro life in Chicago: “There is an open and raw beauty about the city that seems either to kill or endow one with the spirit of life. I felt those extremes of possibility, death and hope, while I lived half hungry and afraid in a city to which I had fled with the dumb yearning to write, to tell my story.”[1]
BLACK MIGRATION | PUBLIC DENIAL
AVAILABLE WITHOUT FREEDOM | In the introduction to Black Metropolis, Richard Wright describes white Chicagoans questioning why Black migrants willingly uprooted themselves from the South, given the racial animosity and rapidly deteriorating built environment of Chicago’s South Side in the early 1900s. Between 1916 and 1970, six million African Americans migrated from the rural South to industrial cities in the Midwest and Northeast. In the first five years of the migration, Chicago saw a 50 percent increase in the Black population—from 46,000 to over 83,000 residents; by 1937, more than 237,100 Black Americans called the South Side home. [2]
Fleeing the Jim Crow South meant the possibility of industrial rather than agricultural work, with the promise of better wages and greater public freedoms to move about the city. Upon arrival however, migrant Blacks were confronted by a different form of public denial. Throughout the Jim Crow era, when separate but equal was the law of the South, northern cities maintained a different form of discriminatory practices perpetuated by white homeowners, real estate agents, lenders, and employers. Racial restrictive property covenants, redlining, and blockbusting formed an impenetrable barrier, intentionally constraining the geographic and economic mobility of Blacks in the city. These practices simultaneously and systematically devalued Black land assets and deepened the narratives of Black inferiority and Black neighborhood undesirability. The new Black Chicagoans found themselves spatially confined to an area that would become the Chicago Black Belt, unable to avail themselves of all the offerings of urban life.
Today, the Black Belt is simply referred to as the South Side. For a Black Chicagoan, growing up on the South Side is to be nourished in Black space, but often with little knowledge of the forced restriction that once bound people together in place. Nonetheless, the South Side now proudly belongs to Black Chicagoans, and their claim is validated by its history of confinement.
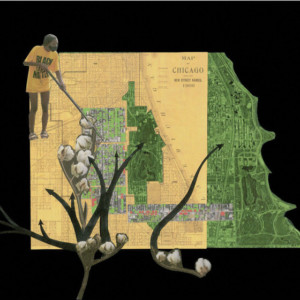
AN UNGUARANTEED EXISTENCE incorporates the three Great Migration routes used by Black Americans to access the greater personal freedoms and fortunes promised by cities outside of the southern states. The routes are intertwined with thorny cotton stalks representing the escape from chattel slavery and journey toward the Chicago Black Belt. Underneath is a 2020 aerial map of the Washington Park and Woodlawn neighborhoods, where over 200 acres of publicly owned vacant land appear as green voids on the map similar to the formal park spaces of the neighborhood. These vacant lands, the byproduct of urban renewal, disinvestment, and Black population exodus from the South Side, are demanding a new form of land care by remaining residents. Today, however, tending the land is not generating wealth for anyone; instead it is a temporary investment of sweat equity to cultivate greater safety, beauty, and mental well-being while residents wait for redevelopment.
Continue reading on the Harvard Design Magazine website…
“South Side Land Narratives: The Lost Histories and Hidden Joys of Black Chicago” by Toni L. Griffin is excerpted from Issue No. 49 of Harvard Design Magazine: Publics.